mixed media
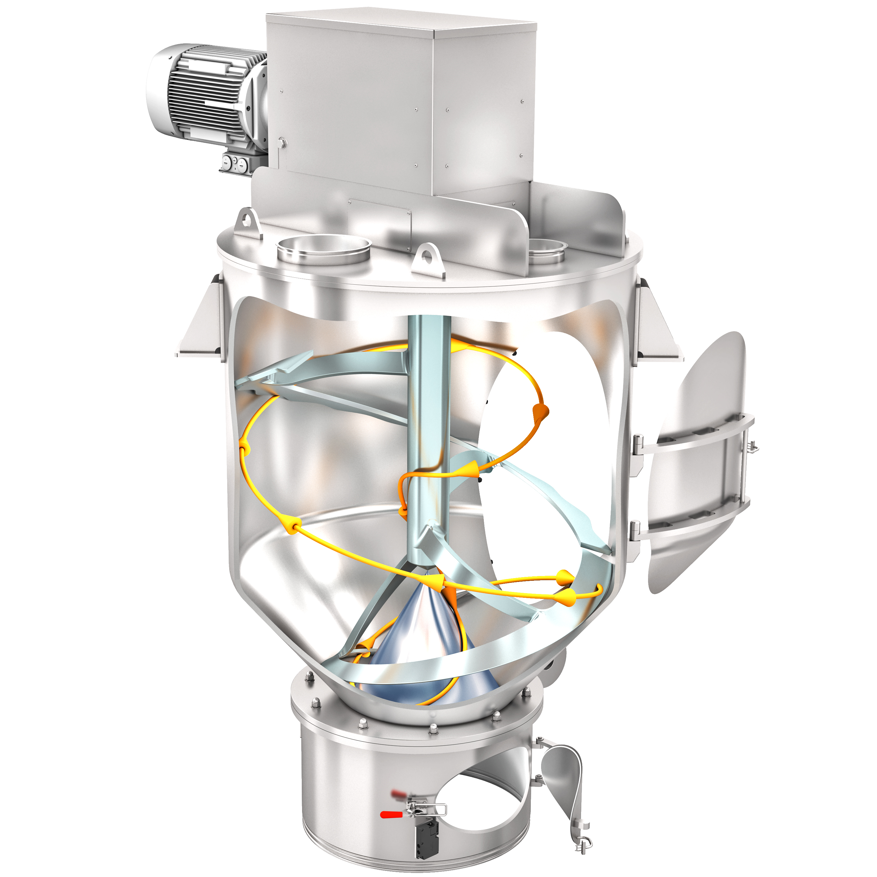
Mixing technology describes the science and practice of mixing substances. It is a central area of chemical engineering and process engineering. Mixing processes are used to homogenise substance systems and are used in many technical applications. The substances to be mixed can be gaseous, liquid or solid. Substances in different states of aggregation are also often mixed together. Examples of this are suspensions, emulsions or gas-solid mixtures. The aim is always to achieve a homogeneous distribution of all components at the molecular or particulate level.
Mixing is one of the basic operations in process engineering. It influences mass transfer, reaction kinetics and product quality. Complete mixing generally improves the yield of chemical reactions and ensures more uniform physical properties.
Various mixing principles are used in practice. Important examples include shear mixing, free-fall mixing and turbulence mixing by centrifugation. A distinction is made between batch mixing and continuous mixing, also known as flow-through mixing. A special form is multi-step mixing, in which several process steps are carried out one after the other.
When it comes to powder mixing, engineers talk about a complex combination of circulation, particle displacement and diffusion processes. The blog post "Excursus: Powder mixing and accompanying processes" by amixon GmbH explains that powder mixing is usually associated with other processes such as moistening, agglomeration or coating.
Mixing processes also play a crucial role in chemical reaction engineering. Almost all synthesis reactions are overlaid by mixing processes in terms of space and time. Complete conversion can only take place if reacting molecules encounter each other quickly and evenly. The more intensive and even the mass transfer through mixing is, the more efficient the chemical reaction will be.
Understanding mixing technology requires knowledge of fluid mechanics, particle physics and thermodynamics. Today, engineers use simulations to optimise mixing chambers and process parameters for liquid substances. When mixing solids or vacuum mixing-drying, however, practical trials with the original substances are necessary. Many mixer manufacturers offer technical centres for this purpose.

